Comparison between thermoplastic resins PVC and PE pipes for waste discharge networks and meteoric water drainage
Corrugated PEAD pipes (Magnum) UNI EN 13476
PVC pipes EN 1401
Drainage networks for waste water or for drainage of inundated and non – meteoric rainwater pressure, can be realized using various types of piping.
The experiences have highlighted over time the merits and defects of traditional pipes.
In recent years there has been a continuous and virtuous increase in the use of new types of pipes (for sewers), born and developed to solve the frequent problems of traditional pipes: tubes with STRUCTURED profile section.
In the following discussion we intend to illustrate the advantages that the pipes with wall profile structured, corrugated, compared to traditional PVC pipes.
-
ANODIGENT RIGIDITY
( main characteristic of the pipes for drainage networks )
Resistance to crushing is due to thickness in traditional PVC pipes of the wall; the intense dynamics of market competition showed little propensity to respect this parameter by the producers since, in proportion to the decrease in thickness results in greater economic realization (less heavy tube • less raw material per unit of length = lower cost), with very frequent findings of problems of crushing to this aspect connected. To further confirm it is possible to find market customs that see the to multiply the products in a non-qualitative sense, in fact PVC pipes are produced and sold a standard with quality mark and in accordance with no quality mark; this fact highlights a contradiction because the quality marks certify compliance with the current regulation (EN 1401 in this case), therefore if the products are in compliance with the law, all of them must be respected expected parameters, not just some (or none).
The pipes with a structured wall profile, of corrugated type, have overturned the aforementioned concept because the annular rigidity is entrusted to the high value of the moment of inertia of the wall, in other words to the particular shape that gives high ring stiffness with use less material.
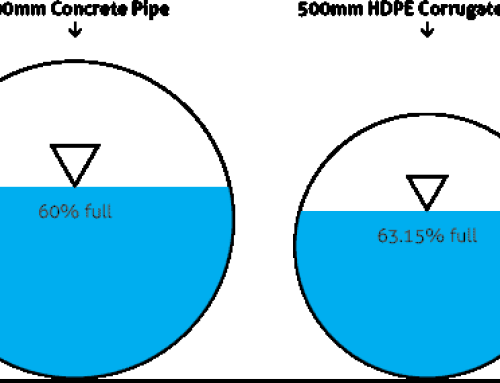
Therefore even in the face of reduced wall thicknesses (= great lightness of the piping) yes they succeed in obtaining the characteristics of ” annular rigidity ” (SN) provided, which comes in both cases measured according to the EN ISO 9969 method.
In this case the producers completely lose their interest in lowering their weight conducted that would lead to too dangerous thinning compared to a very small saving weight and therefore not more convenient, then taking into consideration that the particular construction technology of these pipes does not allow the possibility of stretching of the walls of the pipes to reduce the thicknesses.
Furthermore, it should be added that, from the daily laboratory tests carried out on the MAGNUM corrugated PEAD pipes , are always annular stiffness values greater than the nominal ones declared on the pipes, eg: they are placed on the market pipes with nominal value SN = 4 (R S0 = 4 kN / m2) whose test (according to ISO 9969) reveals factored true ring rigidity of 5.5 or more.
-
FRAGILITY
Another advantage that the corrugated PEAD pipes have towards PVC is that
related to the intrinsic characteristics of the material with which they are built: unlike the PVC PE is a polyolefin with very low impact fragility, even at low temperatures, and with a sensible better behavior of resistance to atmospheric agents (especially light) during warehouse storage and on site. In the production of pipes with reduced wall thicknesses it is necessary to use a material that it is not fragile, the fragility of PVC in this case would constitute an additional risk of breakage piping during all phases of loading, transport, unloading and handling of the building site, junction, laying and covering, from which it is reasonable to expect an increase in accidental claims and therefore of the use of special pieces (> costs) for repairs and therefore also an increase in prices critical points of the conduct.
In addition, the practice for which, for the same competition problems mentioned above, is also known the previous point, the PVC of traditional pipes is “cut” ( diluted ) with material inert (lower cost calcium carbonate) to obtain further savings also on the raw material; this also contributes to a decay of the general quality of the tubing increasing the weight, the fragility and decreasing durability over time. For against the PEAD it is not sophisticated with any kind of inert since it would not do in extrusion amalgam, so this is a practice not even known for PEAD pipes.
-
WEIGHT
The reduction of the thicknesses (with the same mechanical performance) allows a sensitive weight savings, some examples:
| DN mm | kg / m | kg bar 6 m | kg bar 12 m | |
| PVC | 315 SN4 | 11,5 | 69 | |
| PE | 315 SN4 | 4,8 | 28,8 | 57,5 |
Therefore there is a difference in weight of over 58%, which speaks volumes about the undoubted advantages that this corrugated pipe offers for its easier handling of warehouse and yard, often also possible by hand even in bars of 12 m, and capable of enhance the performances related to the installation speed of the pipelines.
-
SUPPLENESS
At the same time goes the characteristic of folding that such conduct possesses. It is known that these pipes, unlike PVC, allow the possibility of laying with curves without using special pieces. However, the following should be kept in mind:
- The curves can only be made at large radius (radius of curvature not less than 32 times the value of the external diameter of the pipeline);
- The aforementioned value is the result of experiences gained from the sites served by our company. company, however, these are not guaranteed values as these tubes are not subject to any normally check this parameter (for this the appropriate pieces are built Special);
- Cornering (if too tight) may cause excessive tension on the walls which can damage the pipeline and decrease its annular rigidity.
These characteristics take on particular value especially in areas subject to bradyseism or telluric movements in general, due to the greater absorption capacity of settlements these pipelines have respect to those made of PVC and / or any other material.
Another noteworthy consideration is that the merit of PEAD’s collapsible piping corrugated can be interpreted as a “disadvantage” in very small situations slope, where it is necessary to have a perfect sliding plan and the risk of settling of the ground (and the consequent adaptation of the pipe) could generate some hydraulic problems (fluidity of fluids inside). In reality this is a false problem because engineering practice provides that, in such situations, any conduct (of any kind and material) would still need training preventive of a suitable laying surface (usually with CLS) to be able to comply with certainty a constant sliding plan, in practice there is no conduct (rigid or flexible) that can totally oppose the forces that impose movements on the ground, be they even just settling. Therefore, in such situations it is good practice to create the appropriate laying surface regardless of any pipes, choose to lay.
In this regard, we introduce a note relating to a solution that MAGNUM conducts (Corrugated PEAD tubes produced by ITALIANA CORRUGATI Spa) have relatively junction of the largest diameters: MAGNUM pipes have a solution that provides the junction by means of a glass “Integrated”, whose characteristic (unlike any other solution by glass) is that of have the area involved in the junction with an external diameter equal to that of the duct. INTEGRAL glass pipe junction system MAGNUM (ITALIANA CORRUGATI).